CLASS Xth SCIENCE
Hello everyone I have attached the updated the class Xth SCIENCE NOTES
Dear student this article about the class Xth education and basically just wanted to release the practice notes .
Every time make sure that the best preparation for the next examination of class Xth and other relevant information about your experience for automatically generated knowledgeable facts zone...
To prepare the class Xth education and basically science chapter wise notes and pdf.. for
CLASS Xth SCIENCE
CHAPTER 06
Life processes – The processes that are necessary for an organism to stay alive. Eg. Nutrition,
respiration, etc.
Criteria of life- (i) Growth (ii) Movement
Nutrition- The process in which an organism takes in food, utilizes it to get energy, for growth,
repair and maintenance, etc. and excretes the waste materials from the body.
Types of nutrition
1. Autotrophic nutrition (Auto =self: trophos = nourishment) E.g. Plants, Algae, blue green
bacteria.
o Process – Photosynthesis(Photo=light; Synthesis= to combine)
o Raw materials- (i) Carbon dioxide (ii)Water
o Equation- sunlight
o 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2
Chlorophyll
o Energy conversion- Light/Solar energy to Chemical energy
o Role off Chlorophyll- To trap the sun‘s energy for photosynthesis
o
Factors-
(i) Carbon dioxide (ii) Water(iii) Light (iv) Temperature
o
Events/ Steps of photosynthesis-
(i) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
(ii) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy & Splitting of water moleculeinto Hydrogen & oxygen
(iii) Reduction of Carbon dioxide to Carbohydrate
o Gaseous exchange- (i) Gas used- Carbon dioxide
(ii) By product - Oxygen
o
Source of raw materials-
(i) Carbon dioxide –Land plants- Air, Aquatic plants- Water
(ii) Water & Minerals - Soil
2. Heterotrophic nutrition (Hetero =others: trophos = nourishment) Eg. Animals, plants
lacking chlorophyll like fungi.
(a) Saprophytic nutrition: Organisms feeds on dead decaying plants or animals material. E.g. Fungi,
Bacteria
(b) Parasitic nutrition: Organisms obtain food from the body of another living (host)
o Endoparasite : Parasite lives inside the body of the host e.g. tapeworm, roundworm.
o Exoparasite : Parasite lives on the body of the host. E.g. lice, leech.
Note- The parasite benefits while the host is usually harmed e.g. Cuscutta-plant parasite (amar bel),
plasmodium (malarial parasite).
(c) Holozoic nutrition: Organism (mostly animals) take in whole food and then digest it into smaller
particles with enzyme. Eg. Amoeba, Paramoecium. Animals, human beings.
o Steps in Holozoic nutrition
(i) Ingestion: taking in of food
.
(ii) Digestion: breaking down of complex food into simpler, absorbable form.
(iii) Assimilation: Utilization of digested food from the body.
(iv) Egestion: Removing undigested food from the body
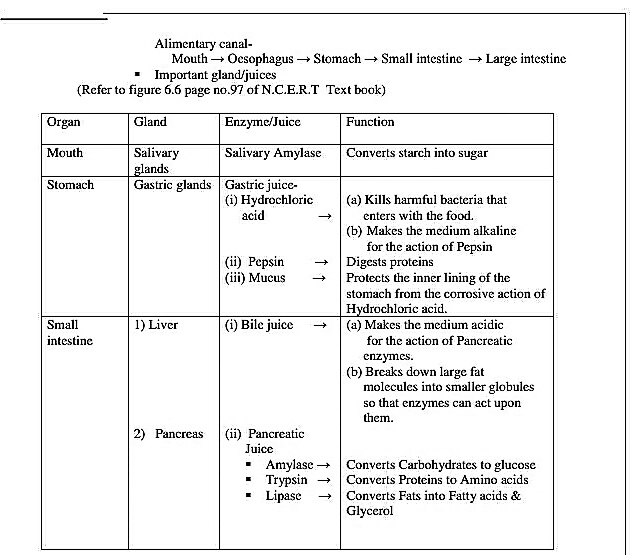
Peristaltic movements- Rhythmic contraction of muscles of the lining of Alimentary canal
to push the food forward.
Sphincter muscle- Helps in the exit of food from the stomach.
Villi- Small finger like projections on the walls of-
(v) Small intestine- To increase the surface area for the absorption of food.
(vi) Large intestine- For absorption of water.
Respiration- The process by which digested food is broken down with the help of Oxygen to
release energy.
o Types of respiration- (i) Aerobic respiration (ii) Anaerobic respiration
o
Some common features of Respiratory organs-
(i) Large surface area- for greater rate of diffusion of respiratory gases.
(ii) Thin permeable walls – to ensure easy diffusion & exchange of gases.
(iii) Extensive blood supply- Respiratory organs are richly supplied with blood vessels for
quick transport of gases.
o
Gaseous exchange in plants-
Process – Diffusion
Direction of diffusion depends
on
(i) Environmental conditions
(ii) Requirement of the plant.
Day time- Carbon dioxide given out during respiration is used for photosynthesis.
Therefore only Oxygen is released, which is a major activity during the day.
Night time – Only respiration takes place. Therefore only Carbon dioxide is released,
which is a major activity during the night.
o
Gaseous exchange in animals-
Terrestrial animals- take Oxygen from the atmosphere.
Aquatic animals- take Oxygen dissolved in water. (Oxygen content is low in water,
therefore they breathe faster.
o Human Respiratory system-
External nostrils ĺ Nasal cavity ĺ Tracheaĺ Bronchi ĺ Bronchioles ĺAlveoli
Rings of cartilage present in the throat ensure that the trachea (air passage) does not
collapse when there is less air in it.
Lungs – (i) Present in the thoracic cavity.
(ii) They are spongy, elastic bags consisting of Bronchi,
Bronchioles and Alveoli
Valves- Unidirectional to prevent the backward flow of blood.
Pulmonary vein is the only vein that carries Oxygenated blood.
Aorta is the only artery that carries Deoxygenated blood.
Double circulation in man- because the blood passes through the heart twice in one
complete cycle of the circulation.
Capillaries- (i) Form the connection between arteries & veins.
(ii) Walls are one cell thick only for easy exchange of
blood.
Platelets- Plug the leaks of arteries and veins by clotting the blood.
Lymph- Extracellular fluid similar to plasma but colourless with lesser protein.
Function of lymph- (i) Transportation of digested & absorbed fats from
the small intestine.
(ii) Drains excess fluid from the intercellular spaces
back in the blood.
Higher animals- E.g., birds, mammals.
(i) Oxygenated blood & Deoxygenated blood are completely separate for
efficient Oxygen supply.
(ii) This is to fulfil higher energy needs and to maintain body temperature
(warm blooded animals).
Amphibians & reptiles- have 3 chambered heat where little mixing of Oxygenated
blood & Deoxygenated blood takes place. Therefore their body temperature varies with
the temperature of the environment. (cold blooded animals)
o Transportation in plants-
Plants need less energy needs- because they do not move and therefore have a slow
transport system
Transport of water-
(i) Takes place by xylem tissue present in roots, stem, leaves and is
therefore interconnected.
(ii) Root cells take up ions from the soil, which creates a concentration
difference between root and soil. Column of water therefore rises
upwards.
In very tall plants- transpiration creates a suction pressure, which pulls the water
upwards.
(i) Helps in upward movement of water in plants.
(ii) It regulates the temperature in plants.
Transport of food-
(i) Takes place by phloem tissue.
(ii) Movement of prepared food in plants is called translocation.
Excretion- The biological process of removal of harmful metabolic wastes in living
organisms.
Download the class Xth SCIENCE CHAPTER 06 pdf click the below link button.....
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JQH5W1skxJHd_DdxqrV1fmwphIUsaVfj/view?usp=drivesdk
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JOB9_y5lj1O8sxYzDEhvSKxFNS3Yb-IJ/view?usp=drivesdk
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JLQNEBZEU9fm5UTjXjYkIYxwIUmwgAR2/view?usp=drivesdk
DISCRIMINATION
Education Zone teams are provided by the best education and preparation for the class Xth education....
MATHEMATICS
SCIENCE
SOCIAL SCIENCE
ENGLISH







Comments
Post a Comment